Highlight Photo
Implications of a Nano-Energy World: Assessment of the Health Risks of Carbon Nanotubes
Examination of exposure levels in terms of number concentration (part./cm) and mass concentration (mg/m) for vertically aligned carbon nanotubes and dispersed single and multi-walled carbon nanotubes
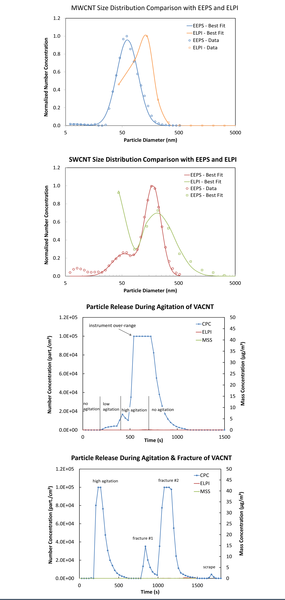
To analyze the environmental, health, and safety concerns surrounding nanomaterials, we examined a nanomaterial touted for use in advanced energy technologies: carbon nanotubes (CNTs). To assess potential health effects associated with CNTs, we conducted a series of experiments to characterize common inhalation exposure mechanisms. The aerosol concentration of vertically aligned CNTs and dispersed single and multi-walled CNTs was measured. The smaller single walled CNTs had a larger aerodynamic size than multi-walled CNTs which adds to the complexity of characterizing their inhalation risk. In addition, a significant release of particles was observed during the shaking and breaking of substrates with CNTs attached. In all cases the particle concentrations were found to be significant on a number but not mass basis. Current OSHA particle exposure limits are only based upon mass concentration which presents a problem for CNT inhalation exposure.
Credits: Golin, Bougher, Mallow, Siviram, Georgia Institute of Technology





